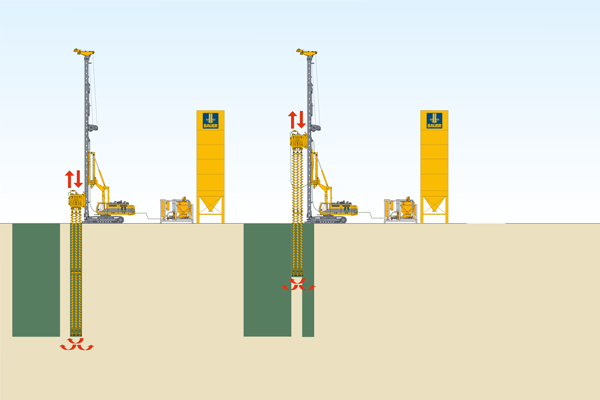
Mixed-in-Place
The Mixed-in-Place method uses rotary drilling or milling methods, which already do not introduce significant vibration into the subsurface through the drilling and mixing process. The existing soil is mixed with cement and additives to form a stable element. The objective of soil improvement is to enhance the compressive and tensile strength, as well as the modulus of elasticity of the soils, per example in and under the tailings facilities and the related dams.
Work procedure and sustainability
To achieve a continuous water barrier and to ensure the homogeneity of MIP walls, in the horizontal direction as well, MIP walls are constructed using the patented double pilgrim step method. This construction method is characterized by additionally mixing of the overlapping areas between primary and secondary cuts. This aims to ensure that along the MIP wall, each wall element has been mixed at least twice. MIP uses the existing natural soils as aggregates. Cement and bentonite are used as construction materials and the soil is not replaced. Therefore, it represents a sustainable solution for cut-off walls.